Europe's New Ariane 6 Rocket Set for First Launch in June-July. Long-Awaited Milestone in European Spaceflight

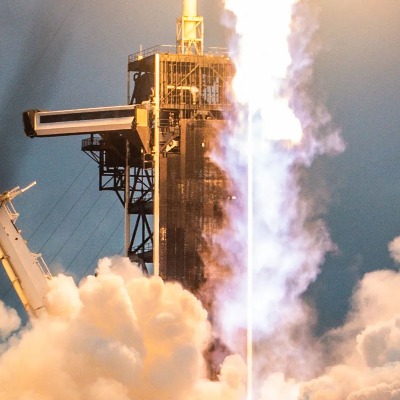
In a significant boost for European space ambitions, the long-awaited maiden flight of the Ariane 6 rocket is now scheduled for June-July 2024, the European Space Agency (ESA) announced on November 30. The announcement comes after a series of delays and setbacks, including the COVID-19 pandemic and technical issues.
The Ariane 6 is Europe's next-generation heavy-lift launch vehicle, designed to replace the Ariane 5 rocket, which was retired in July 2023 after 27 years of service. The new rocket is expected to provide a more versatile and cost-effective launch solution for a wide range of payloads, including satellites for telecommunications, navigation, and Earth observation.
Ariane 6 is a European expendable launch system under development since the early 2010s by ArianeGroup on behalf of the European Space Agency (ESA). It replaces the Ariane 5, as part of the Ariane launch vehicle family. The stated motivation for Ariane 6 (as of 2015) was to halve the cost compared to Ariane 5, and increase the capacity for the number of launches per year (from six or seven to up to eleven).
Ariane 6 is designed with two stages, both powered by liquid hydrogen-liquid oxygen (hydrolox) engines. The first stage has an improved version of the Vulcain engine already used on the Ariane 5, whilst the second stage has a newly designed Vinci engine. Most of the initial lift-off thrust is provided by solid rocket boosters attached to the first stage: either two or four P120s (Ariane 62 and Ariane 64 variants respectively), which are larger versions of the P80s used on the Vega rocket.
Selection of the design concept was made by ESA in December 2014, favouring it over an alternative all-solid-fuel rocket option. Further high-level design was completed in 2015 and the vehicle entered the detailed design phase in 2016. In 2017, the European Space Agency (ESA) set 16 July 2020 as the deadline for the first flight,and in May 2019 Arianespace placed the first production order.
The Ariane 6 is significantly more powerful than its predecessor, with the capability to launch up to 21.6 tonnes (47,660 pounds) of payload into low-Earth orbit. It also features a new engine, the Vulcain 2.1, which is more efficient and less expensive to operate.
The development of the Ariane 6 has been a collaborative effort involving over 400 companies and organizations across Europe. The rocket is manufactured by ArianeGroup, a joint venture between Airbus, Safran, and CNES, the French space agency.
The successful launch of the Ariane 6 will be a major milestone for European spaceflight. The rocket is expected to play a key role in Europe's efforts to maintain its independence in space access and to compete in the global commercial launch market.
Key Features of the Ariane 6
- Payload capacity of up to 21.6 tonnes (47,660 pounds) to low-Earth orbit
- New Vulcain 2.1 engine for improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness
- Ability to launch multiple satellites on a single mission
- Designed for reusing key components to reduce costs
Impact of the Ariane 6
- Strengthen Europe's independence in space access
- Enhance Europe's competitiveness in the global commercial launch market
- Support a wide range of space missions, including telecommunications, navigation, and Earth observation
The first Ariane 6 launch is scheduled to carry the ESA's Comet Interceptor mission, which aims to rendezvous with a comet in 2030 and study its composition and evolution. The mission will provide valuable insights into the formation and early history of our solar system.
The successful development and launch of the Ariane 6 will be a significant achievement for European spaceflight and will pave the way for new and exciting missions in the years to come.